Blood sugar levels show how much glucose is in your blood. Glucose gives energy, but too much or too little can harm your body. Managing it well is key to staying healthy.
Do you often feel tired, thirsty, or dizzy? These could be signs of unbalanced blood sugar levels. Understanding the causes and treatments can help you take control of your health.
Diabetes affects millions worldwide, but it’s manageable with the right approach. Learning about diabetes symptoms, risk factors, and prevention can save lives. Let’s explore how to keep your blood sugar in check and live better.
Key Facts About Diabetes
- Diabetes affects approximately 11.3% of the U.S. population.
- Types of Diabetes: Includes Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes.
- Economic Impact: Annual medical costs for diabetes care in the U.S. exceed $327 billion.
- Fast-growing prevalence: Diabetes diagnoses have increased significantly over the past decade.
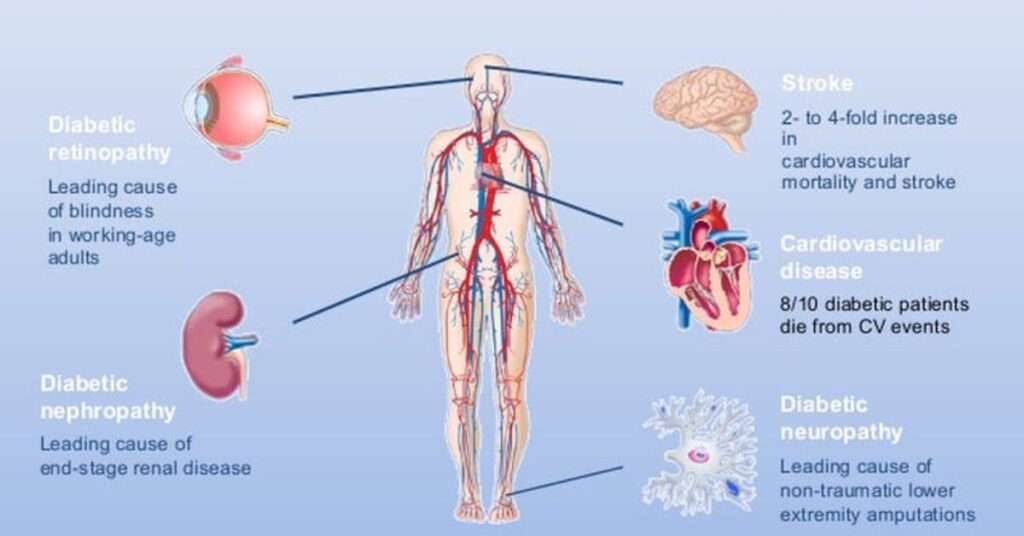
- Diabetes is a leading cause of blindness, kidney failure, and amputations.
You May Also Read This Article: Understanding Climate Change Impacts on Health and Building Public Resilience
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetes?

The symptoms of diabetes can vary, but they often include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, and extreme fatigue. These signs happen because your body can’t manage blood sugar levels properly, leading to high glucose in the blood.
If untreated, high blood glucose can lead to more serious issues like diabetic neuropathy or ketoacidosis. Monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly and being aware of these symptoms can help prevent complications.
Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
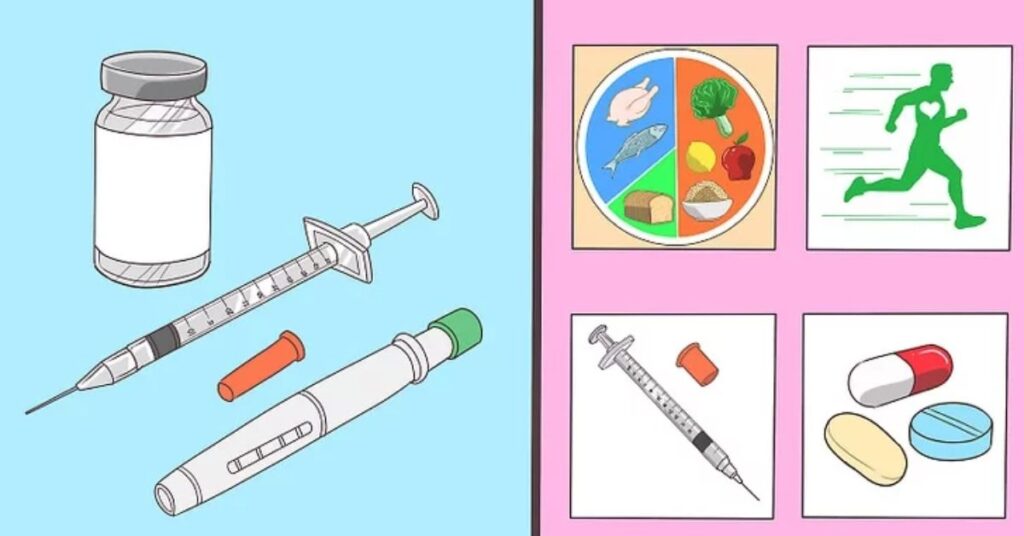
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system attacks pancreatic beta cells, leading to little or no insulin production. On the other hand, type 2 diabetes is often linked to insulin resistance caused by factors such as obesity and a sedentary lifestyle.
Both require diligent diabetes management, although treatments differ. Type 1 diabetes often necessitates insulin injections, while type 2 diabetes may respond well to lifestyle changes and diabetes medication.
| Comparison | Type 1 Diabetes | Type 2 Diabetes |
| Cause | Autoimmune destruction | Insulin resistance |
| Onset | Childhood or adolescence | Adulthood (common) |
| Treatment | Insulin injections | Lifestyle changes, medication |
| Risk Factors | Family history | Obesity and diabetes |
Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes
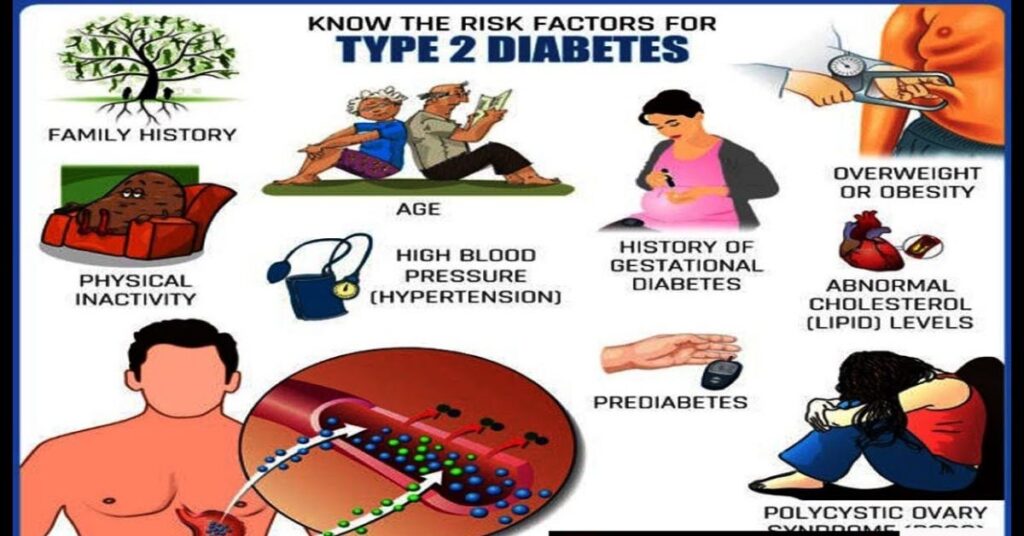
Several diabetes risk factors increase the chance of developing Type 2 diabetes. These include being overweight, having a family history of diabetes, and leading a sedentary lifestyle. People with prediabetes are also at a higher risk, as their blood sugar levels are already elevated but not yet high enough for a diagnosis.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular physical activity and a balanced diet, can reduce these risks. Regular check-ups help catch early signs, ensuring you manage insulin resistance before it progresses to diabetes.
How to Manage Blood Sugar Levels?

To manage blood sugar levels, focus on a diabetes-friendly diet plan that includes low-glycemic foods like whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins. Regular meals and snacks prevent sudden spikes or drops in glucose.
Physical activity plays a major role in improving insulin sensitivity, which helps lower high blood glucose levels. If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, diabetes medication may be needed to help control blood sugar and prevent complications like hypoglycemia.
Best Foods for Diabetics
Choosing the right foods is vital for managing diabetes symptoms. Foods with a low glycemic index, such as berries, oats, and leafy greens, are excellent choices. These foods prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. Avoiding sugary drinks and processed snacks is equally important. For those with gestational diabetes, consulting a nutritionist is critical to maintaining both maternal and fetal health.
| Food Group | Examples | Benefits |
| Fruits & Vegetables | Berries, spinach | Lowers blood sugar spikes |
| Proteins | Chicken, lentils | Improves satiety and muscle repair |
| Whole Grains | Quinoa, brown rice | Steady energy release |
Tips for Living with Diabetes

Living with diabetes means making certain lifestyle changes. Regularly checking your blood sugar levels and sticking to a balanced routine is essential. Staying hydrated and getting enough sleep also contribute to better diabetes management.
Exercise, stress management, and regular medical check-ups are all crucial. By making these habits part of your life, you can keep diabetes complications at bay and enjoy a healthier, more active lifestyle.
Conclusion
Managing blood sugar levels is not just about taking medication; it’s about adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and stress management. By understanding your diabetes symptoms, staying on top of blood glucose levels, and making mindful choices, you can prevent complications from untreated diabetes. Whether you’re dealing with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, or gestational diabetes, taking proactive steps today can make all the difference for a healthier tomorrow.
Remember, diabetes management is a long-term commitment, but it’s entirely possible to live a full, active life with the right support. Regular check-ups, a personalized diabetes diet, and staying informed about the latest treatment options are all crucial in controlling your condition. Keep learning, stay active, and embrace the power of a healthy lifestyle for a better quality of life.
FAQ’s
What are the risk factors of diabetes mellitus?
Risk factors include obesity, family history, age, high blood pressure, and lack of physical activity. Insulin resistance and prediabetes also increase the risk.
What are the types of diabetes mellitus?
The main types are Type 1 diabetes (autoimmune), Type 2 diabetes (insulin resistance), and gestational diabetes (during pregnancy).
What is a strategy to prevent diabetes?
Prevent diabetes by maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, a balanced diet, and managing weight and stress.
What is the explanation of diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition where the body struggles to regulate blood sugar levels, either due to insufficient insulin or insulin resistance.







